Difference between revisions of "Web Forms"
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
:*When using HTML snippets, you'll want to make sure you don't delete any INPUT tags marked HIDDEN or any embedded SCRIPT tags since these are what drive data into your application database | :*When using HTML snippets, you'll want to make sure you don't delete any INPUT tags marked HIDDEN or any embedded SCRIPT tags since these are what drive data into your application database | ||
:*If you include an Email field in the form, the address can be used in email campaigns, allowing the user to register for newsletters, announcements, and product updates. | :*If you include an Email field in the form, the address can be used in email campaigns, allowing the user to register for newsletters, announcements, and product updates. | ||
{{Warn|Since Web Form data can come from external users, it is more likely to contain ''scripts'', which can wind up being executed when the data is displayed. Scripts that are embedded in data strings can be prevented from executing, however, by ''encoding'' data before it is displayed.<br>''Learn more:'' [[HowTo:Protect Your Users by Ensuring that Data Never Executes as Code]] | |||
===Add or Edit a Web Form=== | ===Add or Edit a Web Form=== | ||
Revision as of 23:50, 26 June 2012
Designer > Web Forms
A Web Form is a collection of fields a user can fill in on another site, after which data is sent to the platform. You put a Web Form on your corporate website, intranet, or blog. You can create a version that is ready to copy and customize, or host a form on the platform and send a link to it in an email. However you make it available, you can use it to plug visitor data directly into a platform application.
How Web Forms Work
A Web Form is part of an Object. You generate a Web Form, put it on your site, and when the user enters data, a record is created in that Object. (No database code needed!) An auto-response and/or an email can be delivered to let the user know that the data was received. From there, your Data Policies can take over to initiate additional processing. (For example, send an Order to the fulfillment center.)
Error Handling
In your Web Form, you identify fields that are required. If any information is missing when the user clicks Submit, the error is handled in the form: A message is displayed, and the fields that are missing values are highlighted. Nothing goes to the platform server until all required information is present.
Other errors can occur during "backend" processing on the server:
- A validation error could occur, for example, if a zip code is greater than 99999.
- A Data Policy could throw an exception (accompanied by a message) if an order contains an entry for fireworks in a state where such sales are illegal.
By default, such messages are delivered to the user in a plain page that contains the error message(s), accompanied by a [Return] button that takes them back to the form.
Successful Submission
After successfully submitting data, the user goes to either a page you specify, or to a plain page that acknowledges receipt of the data. (From there, the [Return] button goes back to the original data entry form--so specifying a destination page of your own is almost always a good idea.)
Types of Web Forms
There are two types of web forms you can generate:
- Form Layout - You create a Form in the platform, declaring it to be intended for use as a Web Form. A link to it is generated, for inclusion in your web page. The platform does all of the processing and error handling. This is the easiest kind of Web Form to use.
Learn more: Custom Object Forms
- Form Layout - You create a Form in the platform, declaring it to be intended for use as a Web Form. A link to it is generated, for inclusion in your web page. The platform does all of the processing and error handling. This is the easiest kind of Web Form to use.
- Generated HTML - A complete form is generated in HTML code. You can copy that code into a page on your site and use the default processing, or you can modify it in a variety of ways. For example, you can:
- Take control of the CSS styling.
- Change the layout (for example, to create two columns of field)
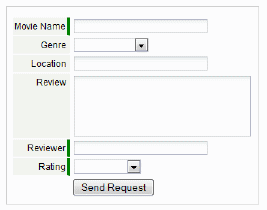
- Change the label of the Submit button. (The default text is "Send Request".)
- Take control of the error handling.
Note: Error handling requires an experienced web designer. To make it work, you get the error page back as data, parse the page to identify the error(s), and then manage the way in which those errors are displayed. It's unlikely that you'll want to go that far, but the capacity is there, if you need it.
Working with Web Forms
Users that have the Customize Objects permission can manage Web Forms.
In the Web Form, you specify the input fields you want to embed in an HTML page. You put the resulting form into the page, and that page is dynamically linked to your application.
Fields in the Web Form are automatically validated according to the rules defined by the application, and you can generate an auto-response to the person submitting the form, or redirect them to a specific URL. You can also notify designated members of your team that someone has submitted the web form.
- Considerations
-
- Web Forms can be created for Custom Objects (and for Prospect objects in the Sales Force Automation application).
- To create a Web Form, the object must be specified as Web-enabled in the Object Properties.
- Web Forms can be disabled in the Object Properties by turning off Web-enabled
- Lookup fields cannot be selected for use in a Web Form
- The Record Owner for a record added by a Web Form can be specified in one of several ways:
- Specify the Record Owner in the settings you specify when you add or edit a Web Form, shown below.
- In a Data Policy, use the Change Record Owner action. (If used, the Data Policy overrides the Web Form setting.)
- In Prospect objects, you can use Assignment Policies to assign record ownership, send trigger email notifications, and generate an auto-response. (If used, those settings override Data Policies.)
Best Practices
Here are some pointers to making web forms work for your business.
- Make sure you have a landing page for people to go to after they fill out the form, since in most cases it is their only confirmation that the submission was a success
- When someone fills in a form, you can automatically email a thank you to them if you include a field of type Email
- Likewise, you can alert a member of your team that someone has filled in the form with a notification - this is great for inquiries that need more interaction
- If you want to fully customize the layout of the form, use HTML snippets instead of the one-line JavaScript as the final format - it gives you more control to layout the form as well as style controls
- When using HTML snippets, you'll want to make sure you don't delete any INPUT tags marked HIDDEN or any embedded SCRIPT tags since these are what drive data into your application database
- If you include an Email field in the form, the address can be used in email campaigns, allowing the user to register for newsletters, announcements, and product updates.
{{Warn|Since Web Form data can come from external users, it is more likely to contain scripts, which can wind up being executed when the data is displayed. Scripts that are embedded in data strings can be prevented from executing, however, by encoding data before it is displayed.
Learn more: HowTo:Protect Your Users by Ensuring that Data Never Executes as Code
Add or Edit a Web Form
To launch the web form wizard:
- Click Designer > Objects > {object} > Web Forms.
- Click the [New Web Form] button, or open an existing web form.
Steps Instructions 1. Format - Enter the Title of this Web Form.
(Only used in the platform. In the list of Web Forms for this Object, it appears in the Name column.) - Choose Type: Form Layout or Generated HTML.
- Form Layout
- A Form created and hosted on the platform is displayed to the user.
A link to it (or a script that accesses it) can be embedded into a web page on your site.- Choose the Form to use
- Select the User who will be designated as the (possibly virtual) person submitting the form.
- The user and the permissions associated with the user's Role may be used determine field and record visibility, and control the layout of the form, based on the form's Layout Rules.
- Specify the label that will appear on the form-submit button.
The default label is "Send Request".
- Generated HTML
- Generates HTML code that can be embedded into a web page on your site.
- You can then modify the layout, or change the label on the button the user clicks to submit the form.
- Specify the URL of the page the user goes to after successfully submitting the form. (Required)
- Click [Next].
- Select Fields
- Select the Object field(s) to include in the web form.
- Click the Required check box next for values the user must supply when filling out the form. (Fields that are identified as "Required" in the Default Layout, or marked "Always Required" in the Field definition are pre-selected automatically.)
- Note:
When you select a File Field or an Image Field, the form automatically includes a file-chooser dialog that lets the user browse for the file to include.
Learn more: Field Display Types
- Click [Next].
2. Notifications - In the Record Owner Information section, select the record owner from the Lookup field.
- Optionally, click the check box to Send Email Notification to record owner when the web form is received.
- Optionally, select additional user(s) to receive the email notification.
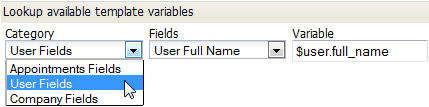
- In the Email Notification Details section, enter the text you want to appear as the Subject of the email. Enter the text you want to appear as the email message in the Description fields. You can customize the message content, and include Template Variables. Use the Template Variable Tool to get the names of variables you can use in the template:
- Click [Next].
3. Auto Response If an email address field was included in the web form, it is a good practice to create an auto response to acknowledge receipt of the web form information. - Complete the following information:
- Email Field (To)
- Choose from None or Email
- If None, no auto response message is sent
- If Email, the Subject and Description fields are required
- Subject
- Description for the auto response email message
- Editor Type (Plain Text or HTML Editor)
- If you select HTML Editor, the HTML formatting tools become available.
- Description
- Enter the body of the message, and optionally include Template Variables.
- Click Next.
4. Click [Save]. HTML code or a link for the form appears, depending on the type of form you chose, along with a Preview. - Enter the Title of this Web Form.
Use the Web Form
- If the Web Form you generated was of type Generated HTML, copy the generated code and paste it into your web page.
Edit it as desired. - If the selected type was Form Layout, both JavaScript and a link are generated.
- The link accesses code stored on the platform. You can copy either one and paste it into your web page.
- When using a link, pre-filled values for selected fields can be embedded in the query-string of the URL by appending them as parameters: &field1=value&field2=value....
- Those variables can be modified dynamically at your site, allowing you to pre-fill different values in different circumstances.
- Special characters (characters other than alphanumerics) need to be encoded.
For example, to include "&" in a value use %26. To include a space use %20.
So for company "A & B" specify company_name=A%20%26%20B.
- Learn more: Specifying Parameters in a URL
- If the Web Form you generated was of type Generated HTML, copy the generated code and paste it into your web page.