Object Relationships
Designer > Data > Object > {object} > Relationships
Objects and their relationships are fundamental concepts of the platform. They are the difference between a flat, two-dimensional spreadsheet and a deep, multi-dimensional process model--one that integrates data management policies and user access rights, in addition to its many other benefits.
Object relationships are shown in the Relationships tab for an object, and are further illustrated in the Sample Order Processing System.
Relating Objects Using Lookups
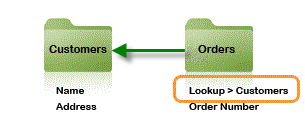
An object relationship is established when one object has a Lookup to another object:
In this example, the Orders object has a Lookup field that references Customers. To create it, it was only necessary to:
- Add a field of type "Lookup"
- Specify the target object (Customers)
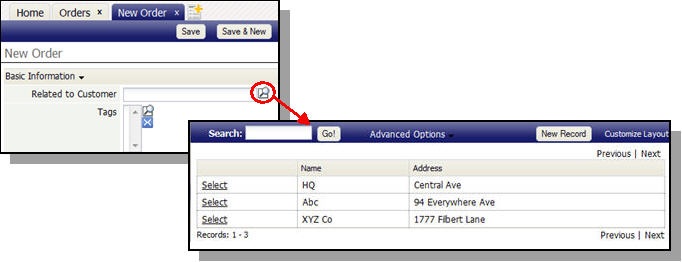
With that relationship established, the platform knows what to do when you create or modify an Order. When creating a new order, for example, clicking the lookup icon (![]() ) gives you a list of Customers you can use to make a selection:
) gives you a list of Customers you can use to make a selection:
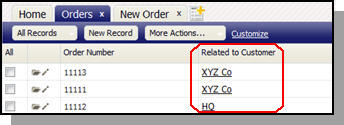
When Orders are displayed, information that identifies the Customer is included:
In each case, you can customize the layout to choose which fields from the Customer record to display, and how they are arranged.
Types of Relationships (Relationship Cardinality)
The cardinality of relationship is determined by the number of possible objects at each end of the relationship.
The possible relationships are:
- Many to One
- One to Many
- One to One
- Many to Many (using an intermediate Junction Object)
Many to One (N:1)
A Lookup field present in an object defines a Many to One relationship. For example, the Orders object has a Lookup to Customers:
So there can be multiple source records (Orders) that point to the same target record (a Customer). So the Lookup defines a Many Orders to One Customer relationship.
- Other Examples of Many to One Relationships
-
- Many employees work for a single company
- Many birds belong to a single flock
One to Many (1:N)
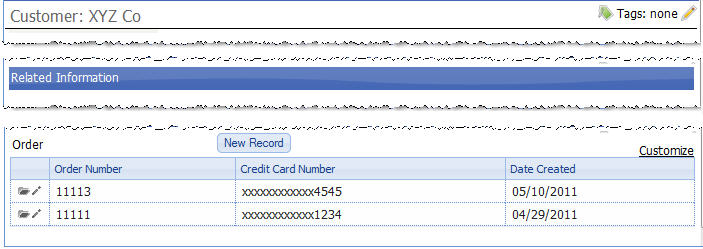
By definition, the "Many Orders to One Customer" relationship also has an inverse relationship: One Customer to Many Orders. The platform handles that relationship in the Related Information of a record. When viewing a Customer record, that section shows all related Orders.
In addition to open Orders, that section shows the history of all Orders for that customer - a time line of your organization's interactions with this Customer, all in one place. Plus, the Related Information Section includes the ability to add Notes and Attachments, Send Email, Add Appointments and Tasks, or Log Activities.
- Other Examples of One to Many Relationships
-
- A person can own many cars
- A car is assembled from many parts
One to One (1:1)
A One to One relationship is considered a special case of a One to Many relationship (1:N). You create a 1:N relationship, and then use the application's business logic to put a lid on the number of source objects, whether that lid is set at one, ten, or a thousand.
Most often, a One to One relationship is best modeled by adding fields directly to the record. But it sometimes happens that there are many fields that are used only rarely. In that case, you can put the seldom-used field in a secondary object, and create a Lookup to it. That makes the information easy to access when you need it, but it doesn't take up time or space (for example, when transmitting record data over the internet).
Many to Many (N:M)
In the Sample Order Processing System an Order can have multiple Tags, and any given Tag can apply to multiple Orders. In that system:
- The tag "Rush" could apply to Order #1 and Order #15. (Many Orders to One Tag)
- Order #1 could tagged as a "Linux" system, while also being a "Rush" order. (Many Tags to One Order)
That arrangement is a Many Tags to Many Orders relationship.
- Examples of Many to Many Relationships
-
- Musicians collaborate to produce songs (and songs can be produced by multiple artists)
- Employees request reimbursement for expenses (and expenses are allocated to employees in a budget)
- Customers place orders for products (and products are purchased by customers)
- Carpools contain different riders (and riders can belong to multiple carpool groups)
Working with a Many to Many Relationship
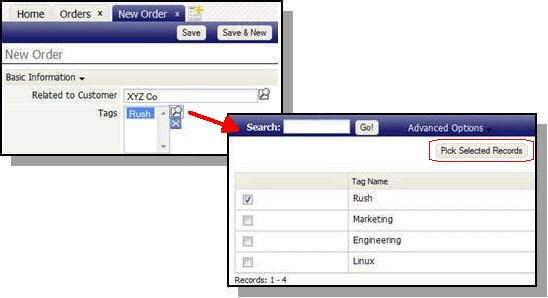
Once a Many to Many relationship has been established, each object contains a Multi Value Lookup field that lets you make multiple selections from the related object. Here, an Order contains a multi value lookup for Tags:
Using the Wizard to Create a Many to Many Relationship
This process establishes a relationship between Tags and Orders:
- Open the Wizard:
- Designer > Data > Objects > [New Object]
- Create Using Wizard
- Create the objects you need.
(At least one object needs to exist, to begin defining a relationship.)- Click the Create New Object icon (
 )
)
- Object Name: - for example, Tags
- [Define Fields]
- Field Label: -- for example: Tag Name
- Click the Create New Object icon (
- Establish Relationships
- Click [Add a Relationship]
- Between: Orders and: Tags
- Relationship Type: Many to Many
An Orders_Tags object is created behind the scenes, and a many-to-many relationship is established.
Note: Programmers who work with APIs will need to know about the Junction Objects that underly Many to Many relationships. Everyone else just needs to know that when they see a strange "Orders_Tags" object in their list of objects, that's just the Junction Object that establishes the Many to Many relationship.
Managing Relationships
The Relationships tab for any given object shows the other objects it is related to. That information is shown in a grid.
Users that have the Customize Objects permission can manage Relationship Information
- Considerations
-
- Lookup fields in the User Object are not editable.
- A Self Reference Lookup in an object will have two entries in the relationship grid (a Many to One relationship and a One to Many relationship).
- An existing relationship can be changed to Many to Many by converting it to a junction relationship. (Learn more: Junction Object#Create a Junction Object Manually.)
Relationships and Composite Objects
Relationship definitions allow for Composite Object operations, where records in related objects can be modified at the same time as the original object, along with objects related to them, and so on--all in a single transaction-safe operation.
- Learn more: Working with Composite Objects